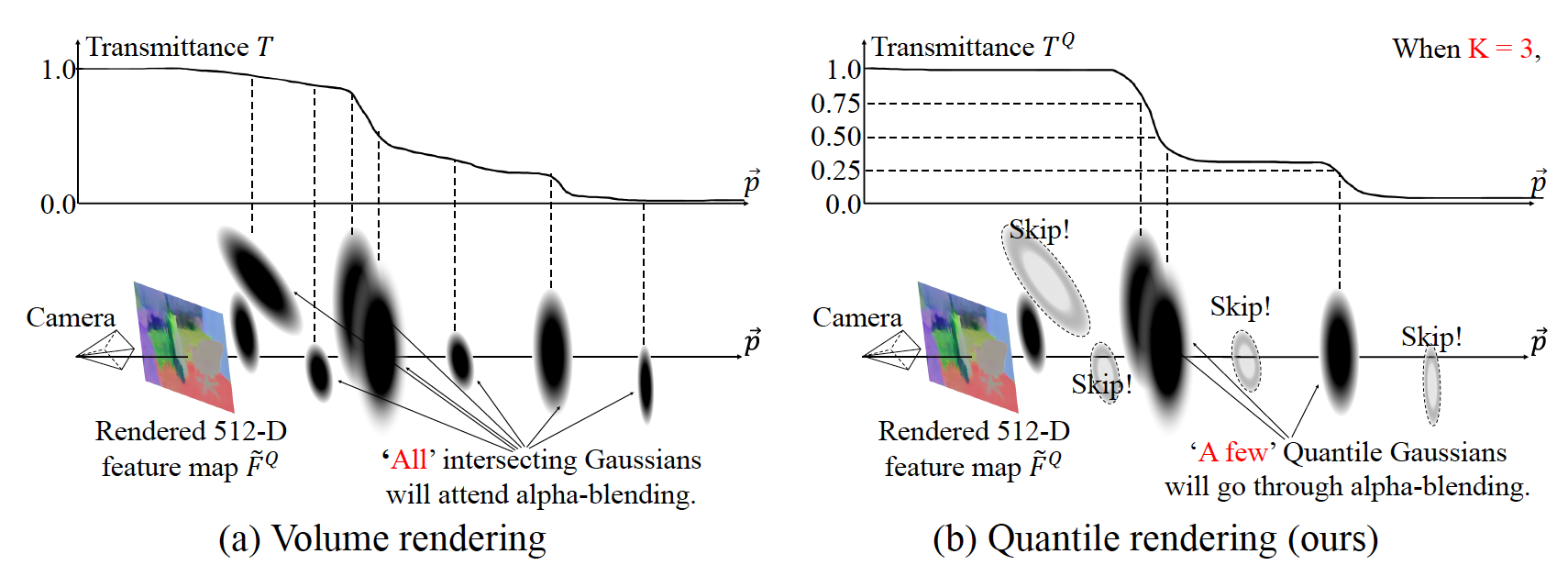
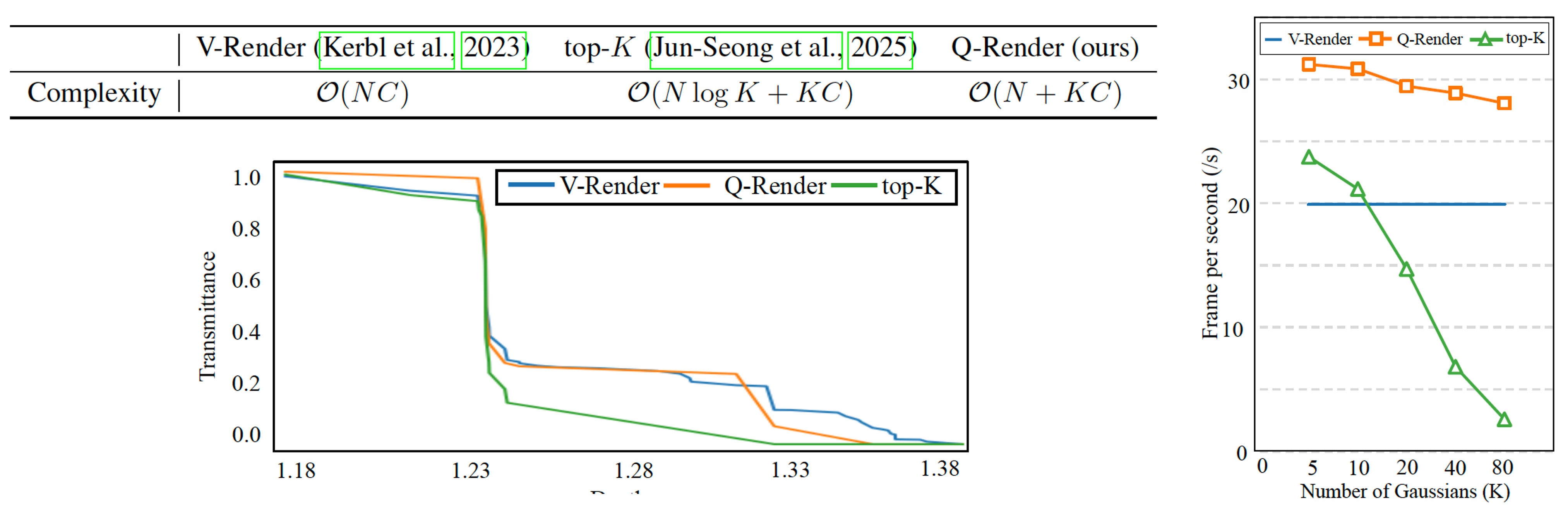
We present Quantile Rendering (Q-Render), an efficient rendering algorithm for 3D Gaussians that involve high-dimensional feature vectors. Unlike conventional volume rendering, which densely samples all 3D Gaussians intersecting each ray, Q-Render sparsely samples 3D Gaussians that have dominant influence along ray. The dominance is determined by transmittance change analysis, and the only sampled Gaussians will participate in subsequent rendering steps such as alpha blending.
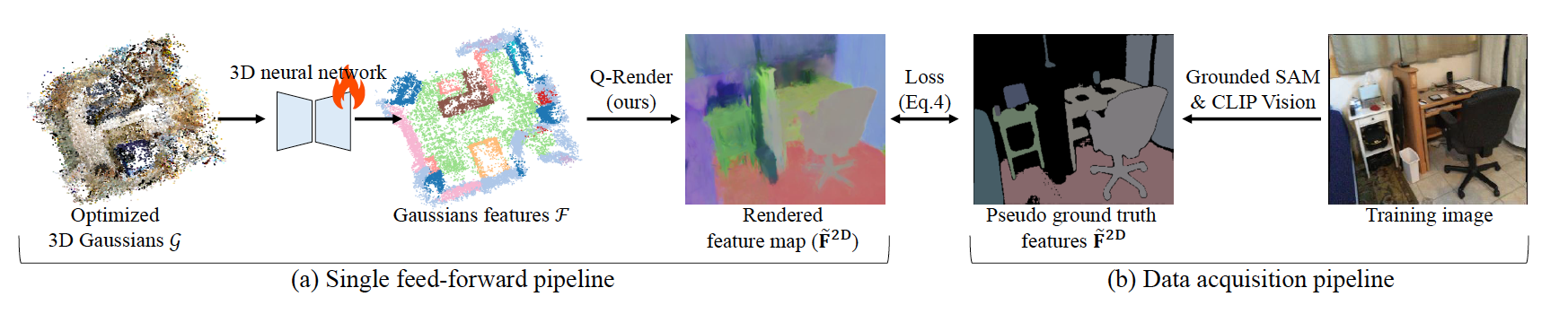
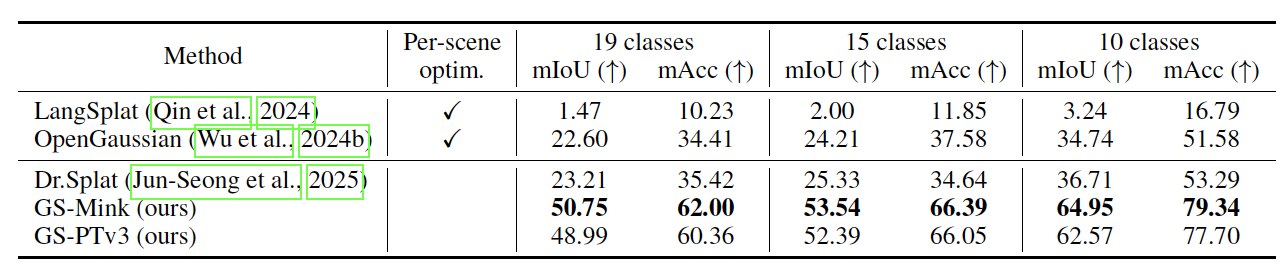
In our framework, Q-Render is integrated with a conventional 3D neural network that operates on 3D Gaussians, named Gaussian Splatting Network (GS-Net), to predict Gaussian features. We evaluate GS-Net on open-vocabulary 3D semantic segmentation using two benchmarks: (1) ScanNet and (2) LeRF-OVS, where 3D Gaussians are enriched with CLIP-based language features. Extensive experiments show that Q-Render under GS-Net consistently outperforms existing methods, achieving superior results and highlighting its potential as an effective bridge between 2D foundation models and 3D Gaussian representations. Furthermore, our Q-render achieves ~43.7× speed gains against previous methods when rendering 512-D feature maps.